
Hip roof framing involves creating a roof with slopes on all four sides that come together at the top. This style is both aesthetically pleasing and effective at shedding water.
Hip roofs are a popular architectural design for residential homes due to their durability and resistance to wind. The frame is constructed from rafters that meet at a central ridge, forming a stable and self-bracing structure. The design often requires additional components such as hip and jack rafters to support the framework.
This type of roofing not only contributes to the overall strength of the building but also provides a sophisticated look. Builders favor hip roofs for their ability to naturally ventilate attic spaces, providing energy efficiency and reducing moisture buildup. Proper construction is essential to ensure that the hip roof is both functional and long-lasting.
Introduction To Hip Roof Design And Framing

Understanding The Hip Roof Structure
The hip roof is a popular architectural style characterized by four sloping sides that converge at the top to create a ridge. Unlike the classic gable roof, which has two sloping sides and two vertical sides creating an “A” frame, a hip roof’s slopes extend from the foundation walls, resulting in no vertical ends. This structure provides enhanced stability and resistance to wind. When approaching hip roof construction, it’s essential to appreciate how each element works in harmony to deliver both form and function.
The Advantages Of A Hip Roof In Residential Construction
Hip roofs are a favourite among residential builders and homeowners alike due to numerous benefits they offer. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Wind Resistance: The slant of the hip roof allows wind to flow over the structure smoothly, making it ideal for high-wind regions.
- Sturdy Construction: The self-bracing design means that hip roofs are innately more stable than other roofing types.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Hip roofs provide a compact and symmetrical appearance, increasing the visual charm of a home.
- Additional Living Space: Depending on the pitch, hip roofs often allow for extra living or storage space in the form of an attic or loft.
- Effective Drainage: The sloping sides of a hip roof promote efficient water runoff, decreasing the likelihood of water damage.

Key Components Of Hip Roof Framing
Hip roof framing involves a number of essential elements that ensure the roof’s integrity and strength. Some of these components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Ridge Board | Horizontal element at the peak where the rafters attach. |
| Common Rafters | Frame from the top of the wall to the ridge, parallel to the building’s length. |
| Hip Rafters | Diagonal rafters that extend from the corner of the building up to the ridge. |
| Jack Rafters | Shorter rafters that join the hip rafters and the wall plate. |
| Valley Rafters | Diagonal rafters that sit inside the corners where two roof planes intersect. |
| Ceiling Joists | Run parallel to the building’s length and tie the walls together while supporting the ceiling. |
Each component plays a critical role in providing the roof its overall shape and structural soundness. Proper calculation and placement of these elements are key to a well-constructed hip roof that can withstand environmental factors and the test of time.
Materials And Tools For Durable Hip Roof Framing
Embarking on a hip roof framing project requires careful selection of materials and tools to ensure a structurally sound and durable outcome. With the right combination in hand, your hip roof will not only offer aesthetic appeal but also the resilience to withstand environmental stresses for years to come.
Selecting The Right Materials For Hip Roof Construction
Material selection is foundational for the longevity of a hip roof. Here are some key considerations:
- Lumber: Choosing the correct grading and type of lumber, such as pressure-treated or engineered wood, is crucial for bearing loads and resistance to decay.
- Roof sheathing: Plywood or OSB provides stability and a base for roofing materials.
- Fasteners: Galvanized or stainless steel nails and screws ensure secure and rust-resistant connections.
- Underlayment: A water-resistant barrier is essential to protect against moisture infiltration.
- Roofing materials: Options range from traditional shingles to metal, each offering distinct durability features.
Essential Tools For Hip Roof Framing
Having the right tools at your disposal can make the hip roof framing process smoother and more efficient. The following are indispensable:
- Carpenter’s square and speed square for accurate measurements.
- Framing hammer and nail gun for securing elements.
- Chalk line for straight and precise lines across the roof surface.
- Circular saw or table saw for cutting lumber and sheathing.
- Level and plumb bob to maintain true and even surfaces.
- Roofing calculator or software to aid in accurate rafter layout.
Innovative Materials To Enhance Durability
To further boost the resilience of your hip roof, consider these advanced materials:
| Material | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Synthetic Underlayment | Offers superior leak protection compared to felt. |
| Metal Roofing | Provides enhanced longevity and fire resistance. |
| Composite Shingles | Delivers exceptional durability and a range of aesthetic options. |
| Reflective Coatings | Improves energy efficiency by reflecting UV rays. |
Whether integrating cutting-edge synthetic underlayments that resist tearing and moisture or opting for eco-friendly cool roof coatings, these innovative solutions can extend the life of your hip roof dramatically.
Step-by-step Guide To Framing A Hip Roof
Embarking on hip roof framing requires precision, a clear understanding of roof design, and a step-by-step approach to ensure a solid and attractive outcome. This guide offers a structured method to tackle each stage of constructing this popular and efficient roof style. Carefully crafted to be both architecturally sound and aesthetically pleasing, the hip roof is an excellent choice for many buildings. Let’s dive into the details, from laying the foundation to the final touches of securing sheathings and underlayments.
Laying The Foundation: Measurements And Markings
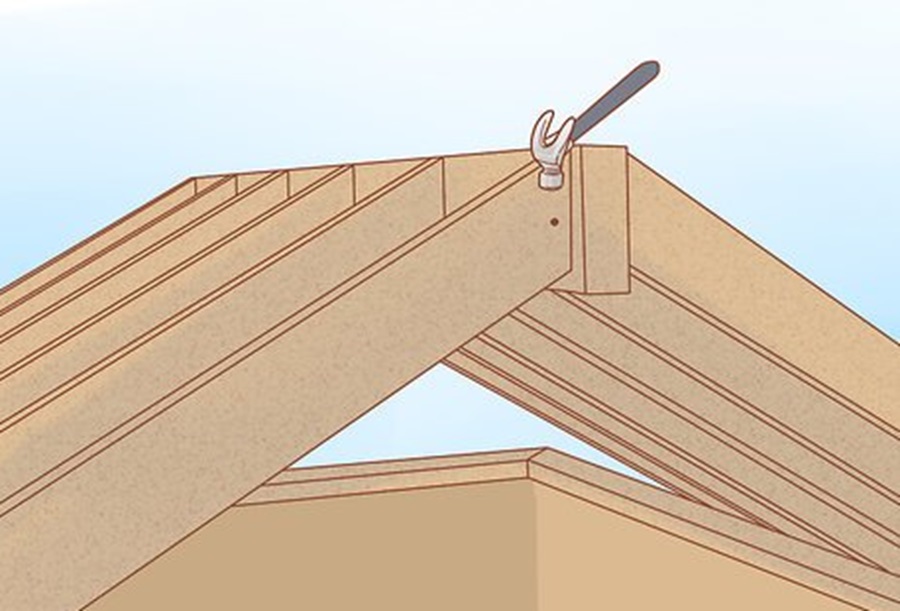
Begin with meticulous planning for a successful hip roof framing experience. Measurements and markings lay the groundwork for precision in every subsequent step. Follow these pointers:
- Create a detailed blueprint reflecting the building’s layout and intended roof style.
- Measure the building’s footprint accurately to determine the length and width of the roof.
- Mark the locations for the hip ends and corners where rafters will meet.
- Ensure all angles are properly calculated and marked for the hip rafters—typically, a 45-degree angle where the rafters slope towards the corners.
Constructing The Common Rafters
The framework of a hip roof begins to take shape with the construction of common rafters. These straight rafters form the “backbone” of the roof, extending from the peak to the external walls. Optimize this phase with the following steps:
- Cut rafters to length, considering the pitch and span of the roof.
- Notch rafters, or “birdsmouth,” to fit securely over the building’s top plates.
- Erect them perpendicularly to the ridge beam and the exterior walls.
- Fasten each rafter in place with galvanized nails or timber screws to maintain a solid structure.
Installing The Hip And Jack Rafters
The distinctive slopes of a hip roof come from the installation of hip and jack rafters. This process involves precision cutting and an understanding of complex angles. Progress as follows:
- Identify and cut the hip rafters, which run diagonally from the building’s corners to the ridge.
- Cut jack rafters, which are shorter, to fill in the space between hip rafters and the common rafters.
- Place hip rafters at a 45-degree angle from each corner of the building towards the ridge.
- Adjust the jack rafters to connect the hip rafters to the common ones—ensuring the entire system ties together securely.
Sheathing And Underlayments: Securing The Base
After structurally completing the rafters, the focus shifts to laying a firm base with sheathing and underlayments. This layer forms the weather-resistant barrier protecting the home. Perform the sheathing effectively by:
- Covering the rafters with plywood or OSB (oriented strand board) panels as sheathing.
- Ensuring the sheathing is nailed down securely, following localized building codes for nail size and spacing.
- Applying an underlayment, such as felt or synthetic materials, over the sheathing for an additional protection layer.
- Ensuring the underlayment is properly overlapped and secured, to provide excellent water resistance.
Advanced Techniques For Enhanced Hip Roof Durability
Welcome to our deep dive into advanced techniques for enhancing the durability of hip roof framing. Known for its sloping sides and lack of vertical ends, the hip roof’s architecture provides aesthetic appeal and excellent resistance to wind. But what about its durability? Ensuring your hip roof stands the test of time requires more than just standard design; it calls for meticulous attention to load distribution, weatherproofing, insulation, and ongoing maintenance. Let’s explore some of the expert-level strategies to extend the lifetime of your hip roof:
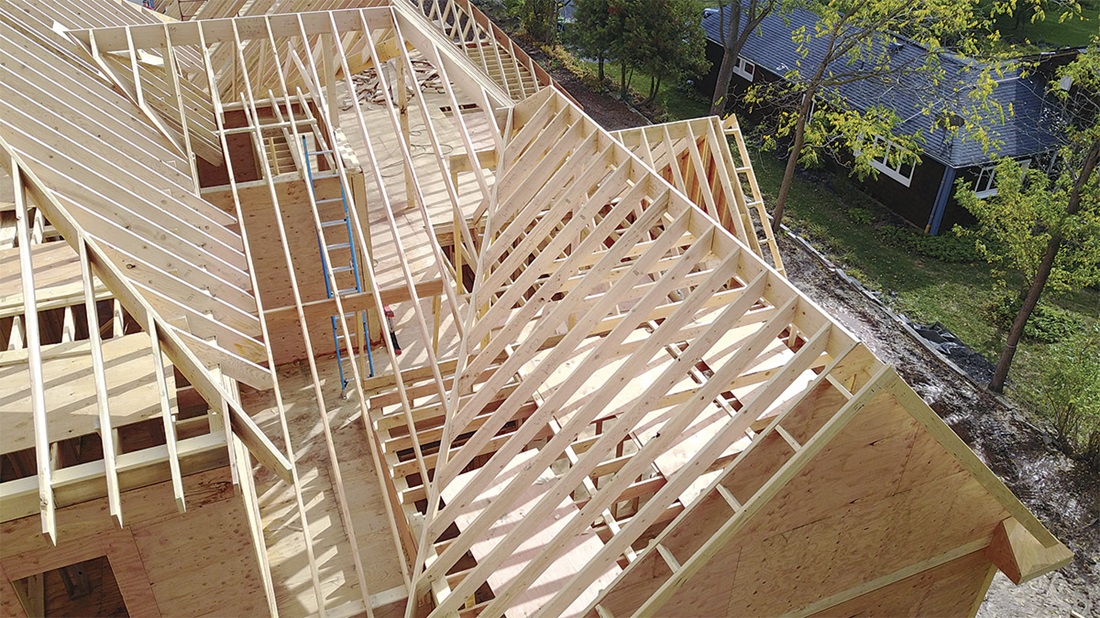

Improving Load Distribution In Hip Roof Framing
A well-structured hip roof begins with optimized load distribution. Ensuring that the weight is evenly spread across the frame prevents stress points, which could lead to damage and eventual failure. Here are several techniques that can reinforce load balancing:
- Use of Diagonal Bracing: Diagonal bracing can transfer loads more efficiently throughout the structure, providing stability against lateral forces such as wind.
- Installing Strongback Braces: These braces join the ends of rafters, effectively tying the roof together and reducing the load on individual members.
- Selecting High-Quality Materials: The choice of wood can make a significant difference. Species like Douglas fir or Southern Yellow Pine offer higher strength-to-weight ratios, perfect for enduring heavy loads.
Weatherproofing And Insulation Strategies
Protection against the elements is critical for enduring hip roof structures. The integration of advanced weatherproofing and insulation techniques can significantly extend the roof’s lifespan by preventing moisture ingress and maintaining thermal efficiency. A multi-tier approach includes:
- Using Synthetic Underlayment: A high-quality synthetic underlayment adds an extra layer of protection against water penetration.
- Applying a Water and Ice Shield: Critical in preventing ice dam formation, this shield is a must-have in cold climates.
- Sealing Joints and Seams: All joints and seams should be properly sealed with roof cement or tape to prevent leaks.
- Optimizing Attic Ventilation and Insulation: Proper ventilation and insulation ensure heat doesn’t build up, reducing the risk of ice dams and helping maintain a consistent temperature.
Long-term Maintenance And Care For Hip Roofs
Regular maintenance ensures issues are detected and remedied before they escalate into significant problems. Establish a routine that includes:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct bi-annual inspections, especially after extreme weather events, to assess and repair any damages that may have occurred.
- Cleaning Gutters and Downspouts: Keep these clear to prevent water backup and potential damage to the roof structure.
- Trimming Overhanging Tree Limbs: Reducing the risk of physical damage from falling branches is essential for the longevity of your roof.
- Monitoring for Pests: Insects and small animals can cause unexpected deterioration; stay vigilant and address any infestations promptly.

Common Challenges And Solutions In Hip Roof Framing
Hip roof framing offers a sophisticated aesthetic with excellent drainage properties, making it a favored choice amongst architects and builders. However, mastering the construction of a hip roof presents an array of challenges, from geometric complexities to durability concerns. Understanding these obstacles and implementing effective solutions ensures the creation of a strong, enduring structure even in the face of nature’s unpredictability. This section explores the common hurdles encountered during hip roof framing and offers practical advice on how to navigate these issues successfully.
Navigating Tricky Angles And Irregular Planes
One of the key difficulties in hip roof construction is managing the intricate angles and varied planes. This complexity demands precise calculations and cuts:
- Utilize advanced software to simulate and calculate exact measurements before executing cuts.
- Implement adjustable roofing squares and bevel tools to measure and mark hip and valley rafters accurately.
- Construct full-scale templates for tricky angles to ensure replication of precise cuts on multiple rafters.
By addressing these angular challenges with meticulous planning and the right tools, the structural integrity of the hip roof can be assured.
Overcoming Material Limitations And Structural Concerns
Material selection and structural integrity are pivotal in hip roof framing, as the wrong choices can lead to premature failure:
- Select high-quality lumber that can withstand the stress of angled cuts and support the roof’s weight.
- Incorporate support elements like steel straps and hurricane ties to reinforce joints, especially in areas prone to high winds or seismic activity.
- Ensure proper load distribution by aligning hips, valleys, and ridges directly over support walls and beams.
Combating material and structural limitations is possible with careful selection of reinforcements and adherence to load-bearing principles.
Tips For Ensuring Longevity In Harsh Climatic Conditions
Harsh weather can significantly shorten the lifespan of a hip roof without the right preventative measures:
- Choose appropriate roofing materials such as metal or asphalt shingles that offer resistance to extreme weather.
- Apply a weather-resistant barrier beneath the roofing materials to protect against moisture penetration.
- Introduce adequate ventilation within the roof structure to prevent heat and moisture buildup that can deteriorate materials.
Meticulously sealing all possible entry points for moisture and regular maintenance checks will impede the wear-and-tear process, thus ensuring the roof’s longevity.
In hip roof framing, foresight and practical knowledge are the blueprints for success. Tackling each unique challenge with the right approach turns potential setbacks into achievements that stand the test of time and the elements.

Conclusion: Best Practices For A Lasting Hip Roof
A hip roof’s durability and functionality rely heavily on its construction. By following best practices in framing techniques, emphasizing quality workmanship, and keeping an eye on future construction trends, a well-built hip roof can provide aesthetic appeal and withstand the test of time. Let’s dive into the essentials for making sure your hip roof stands as a paragon of resilience and architectural beauty.
Read also: Gable Roof Porch Addition_ Enhance Your Home’s Charm!
Summary Of Hip Roof Framing Techniques
The framing of a hip roof begins with precise measurements and cuttings of rafters and trusses, ensuring they fit snugly together to form a stable structure. A combination of common rafters, hip rafters, and jack rafters join forces to present a roof that not only looks good but also effectively disperses weight and withstands external pressures. Some key techniques include:
- Using a framing square to calculate angles and lengths accurately.
- Ensuring that the hip ridge is perfectly aligned with the rest of the structure.
- Applying strong, durable fastening materials to secure the rafters.
The Importance Of Quality Workmanship
Even the best materials can fail if not assembled with precision and care. Quality workmanship is paramount for a hip roof that lasts. This level of craftsmanship entails:
- Meticulous attention to detail throughout the framing process.
- Employment of experienced roofers who understand the intricacies of hip roof construction.
- Regular inspections and maintenance to ensure the ongoing integrity of the roof.
Professional installation contributes significantly to the roof’s longevity, making it imperative to choose contractors with a proven track record.
Future Trends In Hip Roof Construction
As we embrace modern building technologies, hip roof construction also sees advancements. Sustainable materials and eco-friendly designs are becoming pivotal in the architectural scene. Innovations to look out for include:
| Future Trend | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Green roofing systems | Improves insulation, reduces energy costs |
| Integrated solar panels | Enhances energy efficiency, decreases carbon footprint |
| Prefabricated trusses | Ensures quality, optimizes construction time |
Staying abreast of these trends ensures that your hip roof not only serves its purpose today but is also prepared for the environmental and technological demands of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions For Hip Roof Framing
What Is Hip Roof Framing?
Hip roof framing is a construction technique for a roof where all sides slope downwards to the walls, typically with a gentle slope, forming a ridge at the top.
What Are The Disadvantages Of A Hipped Roof?
Hipped roofs offer less attic space and can be more expensive to build due to their complex design and additional materials required. Their intricate structure may also lead to higher maintenance costs.
What Is The Difference Between A Pitch Roof And A Hip Roof?
A pitched roof slopes downwards, typically in two parts at an angle from a central ridge. A hip roof has slopes on all four sides that converge at the top.
Can You Truss A Hip Roof?
Yes, you can truss a hip roof. It involves framing with specialized hip trusses to create the sloping sides.
Conclusion
Mastering hip roof framing can elevate both the durability and aesthetics of your construction projects. By embracing this technique, you ensure a timeless design that withstands the elements. Equip yourself with the right tools, knowledge, and a clear plan to achieve standout results.
Embrace the challenge and watch your roofing skills soar to new heights.

